JavaScript Unwrapped (Part II): Understanding let, const, var, and Operators
Topics: Understanding let, const, var, Operators & Truthy/Falsy Values
Introduction: Unveiling the Power of JavaScript - Understanding let, const, var, and Operators
Welcome to the second article in our JavaScript series! In the previous article, we laid the groundwork by diving into the basics of variables and data types. Now, it’s time to dig deeper into how you can control and manipulate your data using some of JavaScript's most important tools: let, const, and var, along with operators.
Variables in JavaScript can be declared in different ways, and understanding the differences between let, const, and var is crucial for writing clean, efficient, and bug-free code. These keywords dictate how and where your variables live, how they can be changed, and the scope of their influence.
But knowing how to store values is just the beginning. To really make your code do something, you’ll need to harness the power of operators—tools that allow you to perform calculations, compare values, and execute logic.
In this article, we'll break down:
The differences between
let,const, andvar, and when to use each.How to use operators to perform a variety of tasks, from basic arithmetic to complex logical operations.
By the end of this article, you'll have a deeper understanding of how JavaScript handles variables and how you can use operators to bring your code to life. Let’s dive in!
Mastering Variable Declarations in JavaScript: let, const, and var
When writing JavaScript, choosing how to declare your variables can impact the behavior of your code in unexpected ways. JavaScript offers three ways to declare variables: let, const, and var. Each comes with its own rules for how and where the variables can be used, and understanding these differences is key to mastering JavaScript. Let’s dive into each one and see how they work!
1. let - The Flexible One
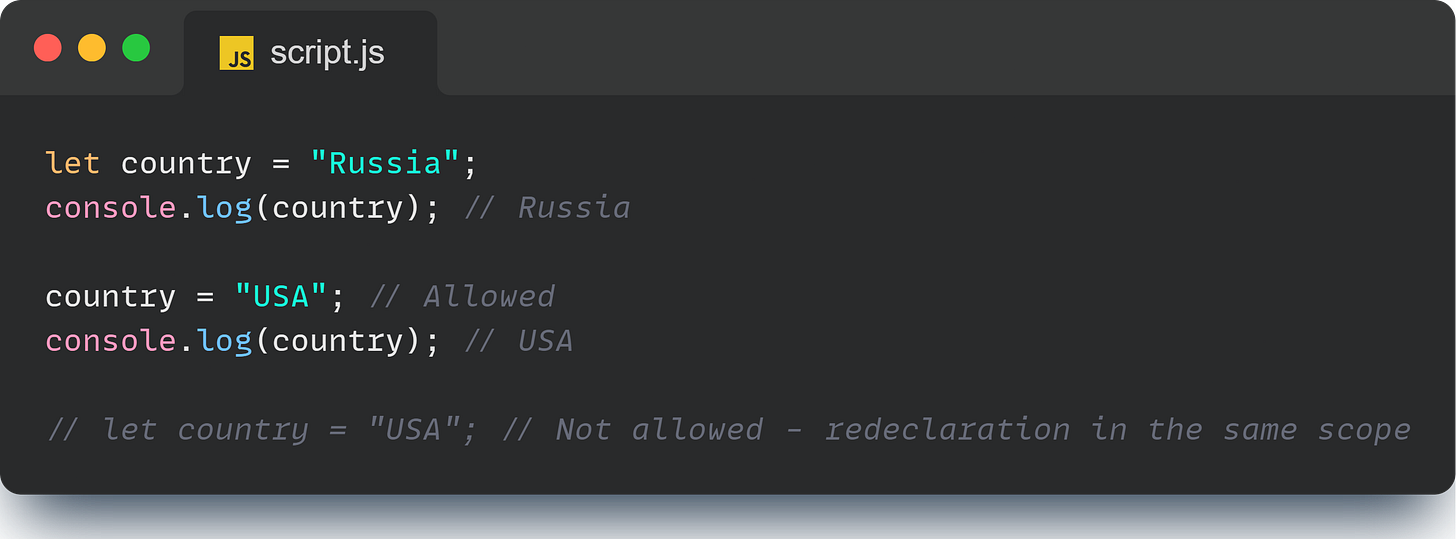
The let keyword is like that friend who’s always there when you need them but respects your boundaries. You can reassign a value to a let variable, but you can’t redeclare it in the same scope.
(Don’t panic if you are new and have no knowledge of scopes in JS. I will cover scope and scope chain in this JS article series. Once you understand scopes, come back here and definitely, you will have a more clear picture!)
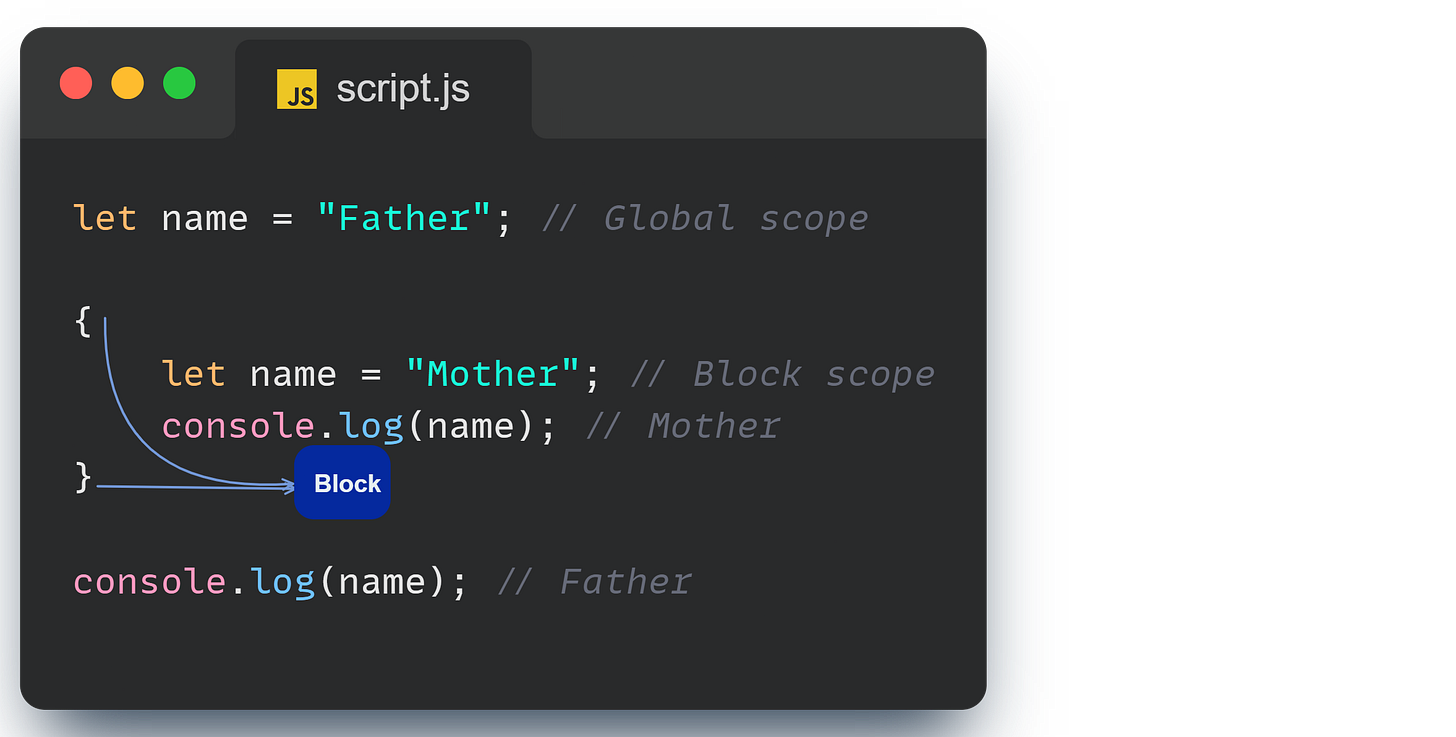
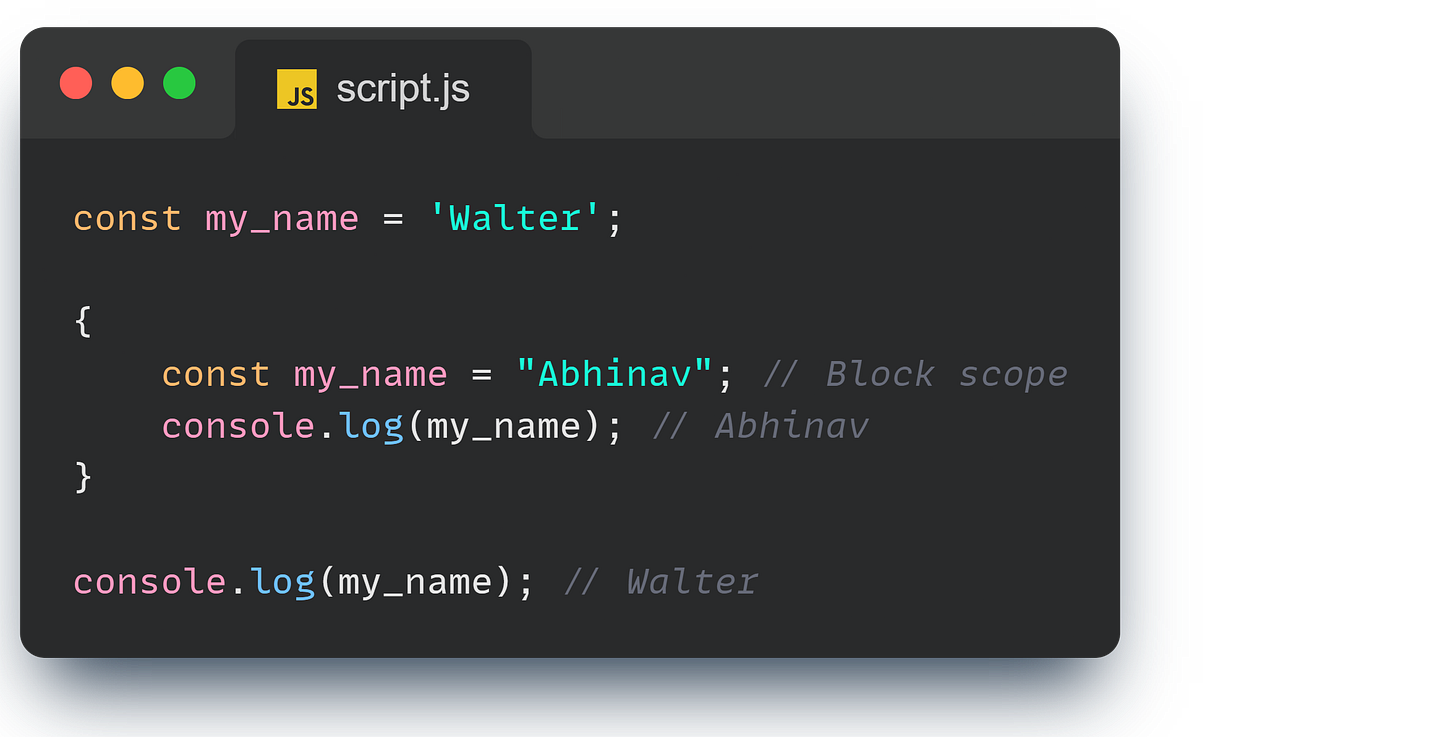
One of the coolest things about let is that it’s block scoped. This means that if you declare a variable inside a block (like within {}), it stays inside that block.
(Note: don’t use name as a variable name - it’s deprecated by JS)
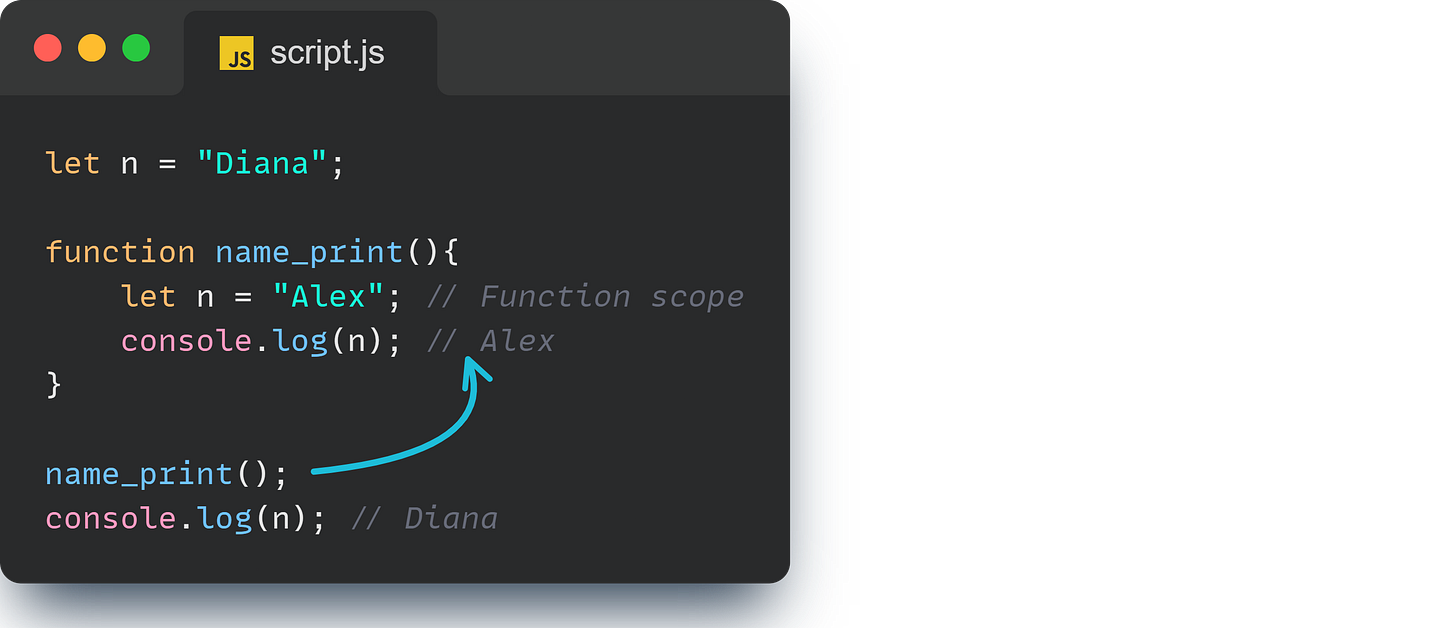
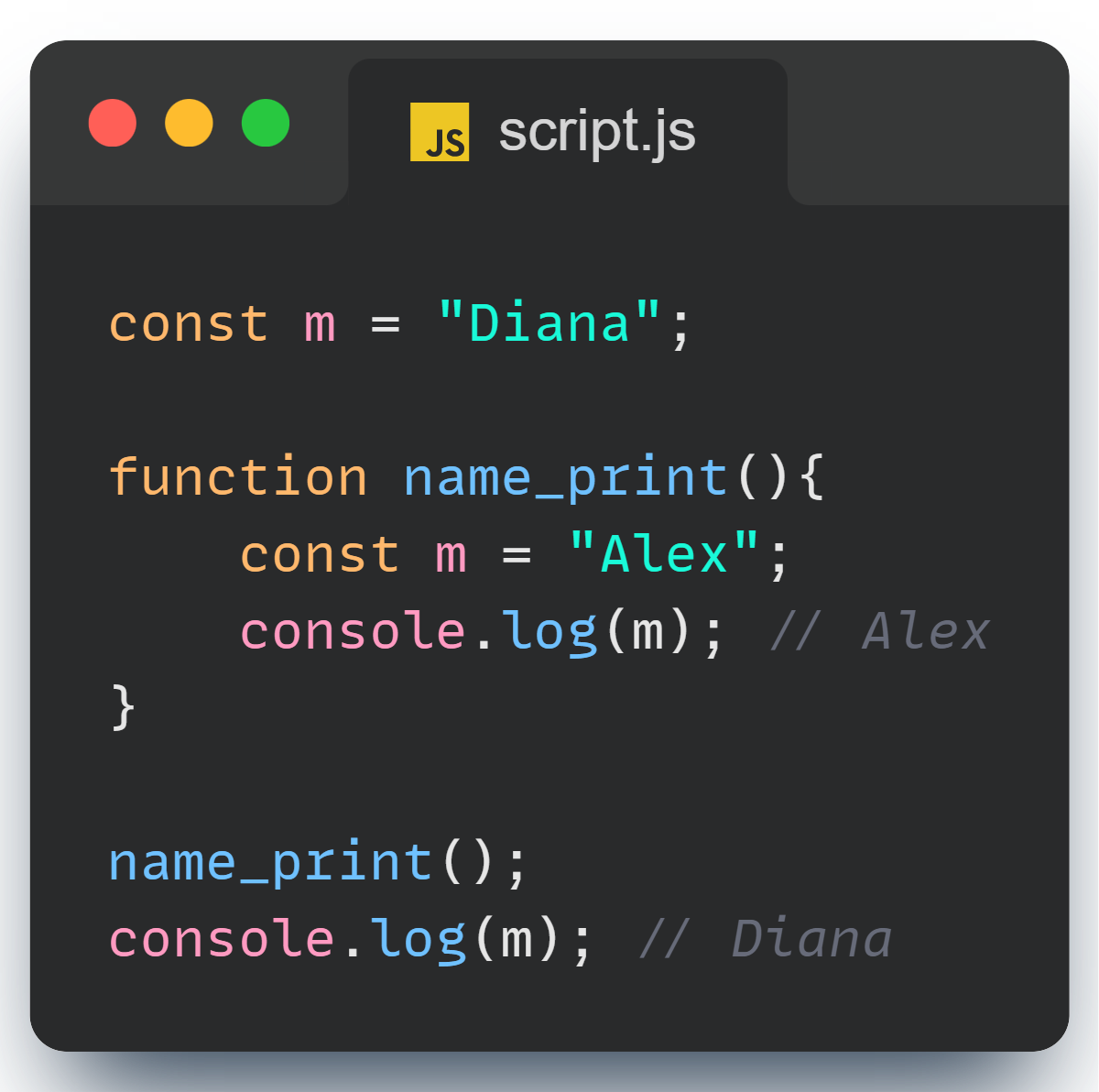
Even inside functions, let respects the scope:
2. const - The Immutable One
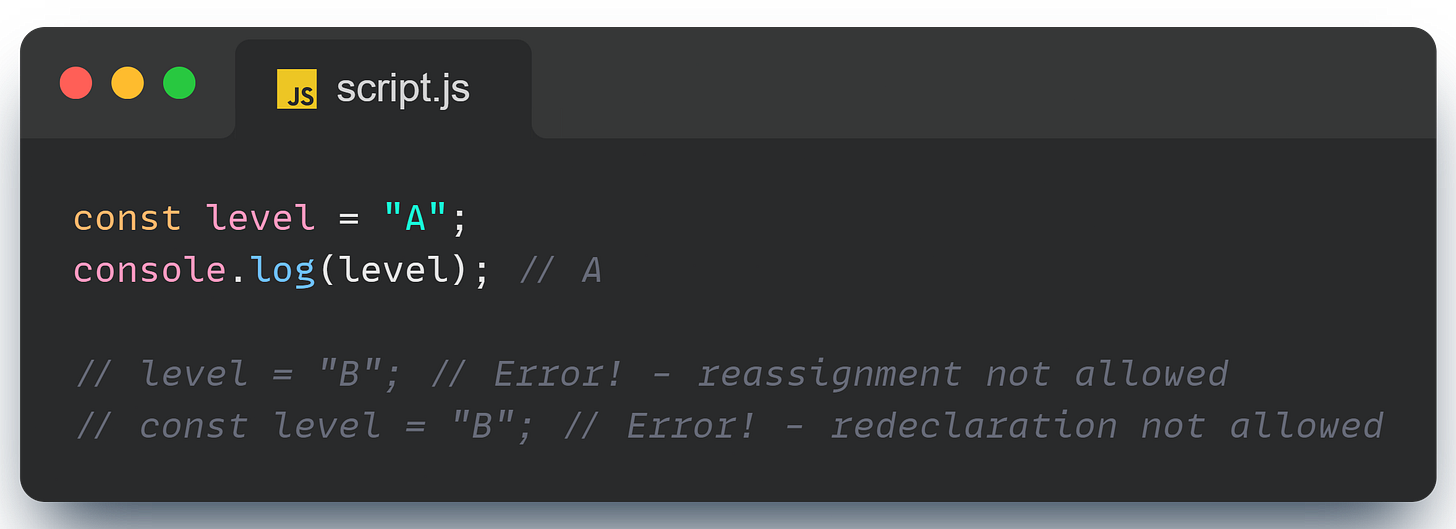
If let is flexible, const is the steadfast one. Once you assign a value to a const variable, you can’t change it—no reassignments, no redeclarations. const is also block scoped, just like let.
const shines when you want to make sure that a value stays constant throughout your code. Like let, const is also block scoped.
Even in functions, const variables stay true to their values:
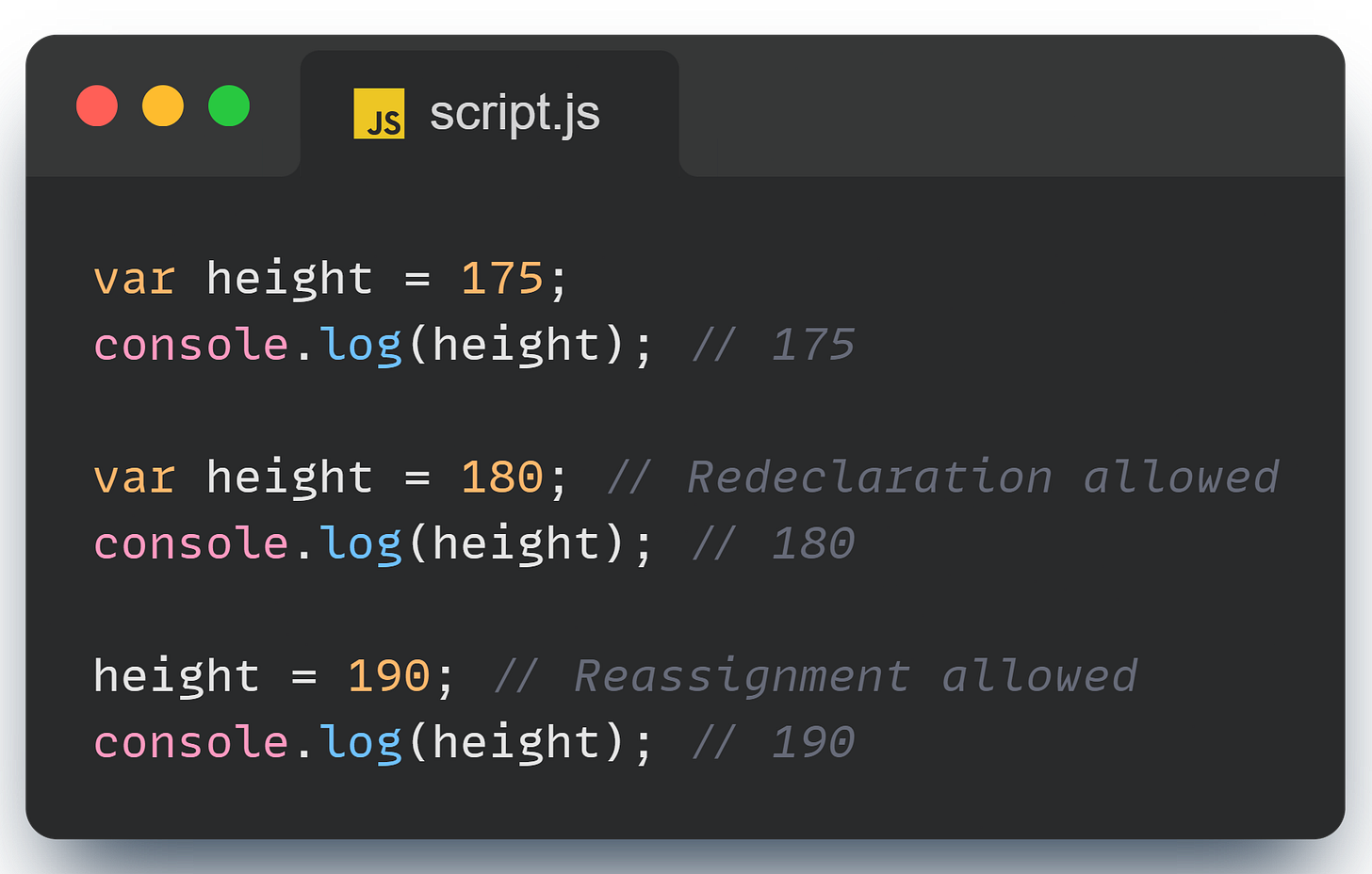
3. var - The Old-School One
Finally, there’s var, the original way to declare variables in JavaScript. Unlike let and const, var is function scoped, meaning it’s only limited to the function it’s declared in. But within that scope, you can redeclare and reassign it as many times as you want.
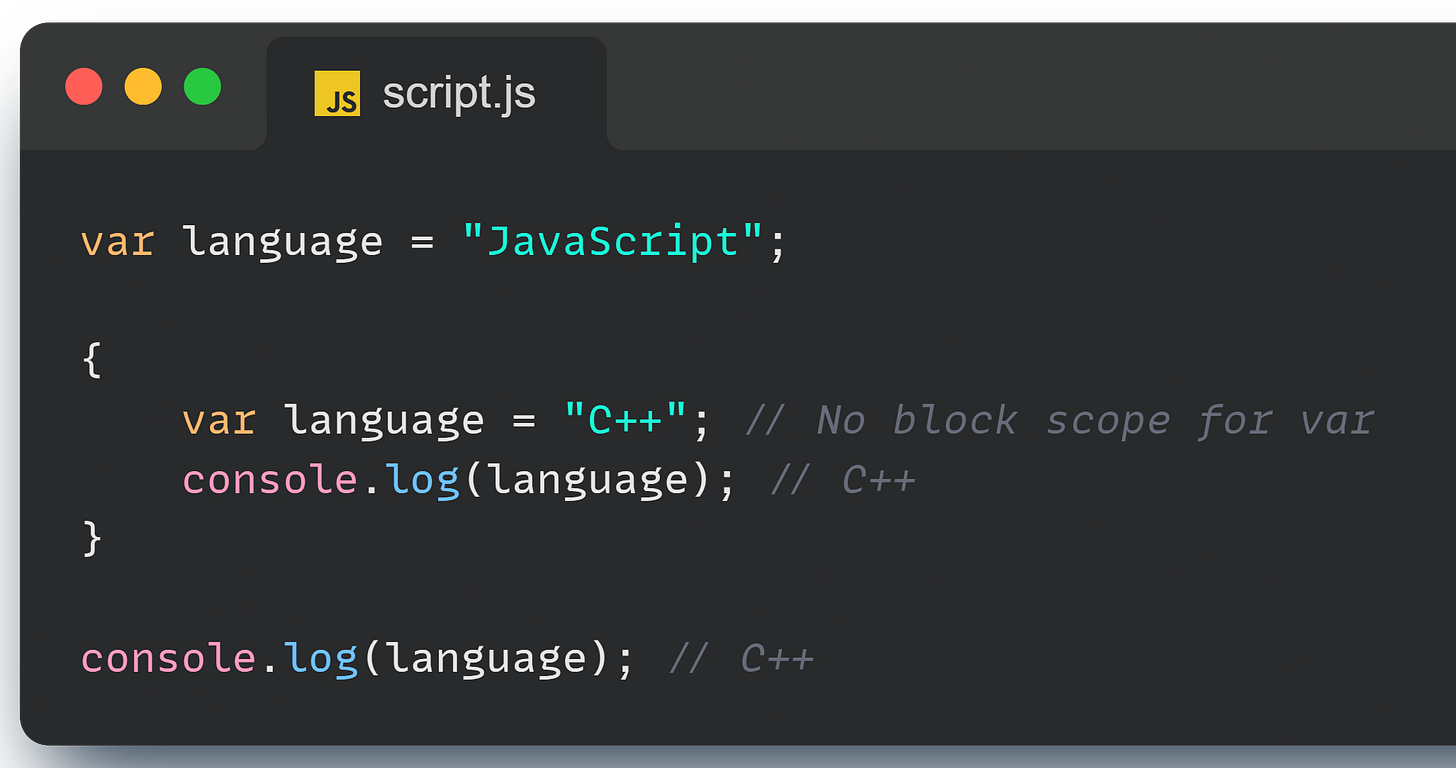
One quirky thing about var is that it’s not block scoped—a var variable declared inside a block can be accessed outside of it:
And here’s something interesting: if you check the global scope in your browser console by typing console.log(this), you’ll see that variables declared with var (like height and language) show up in the global scope. This will come in handy later when we talk about objects and the this keyword in different contexts.
In Node.js, the global scope behaves a bit differently compared to the browser environment. Variables declared with var inside a Node.js module don’t automatically attach themselves to the global object, like they do in the browser. Instead, they are scoped to the module.
Operators in JS
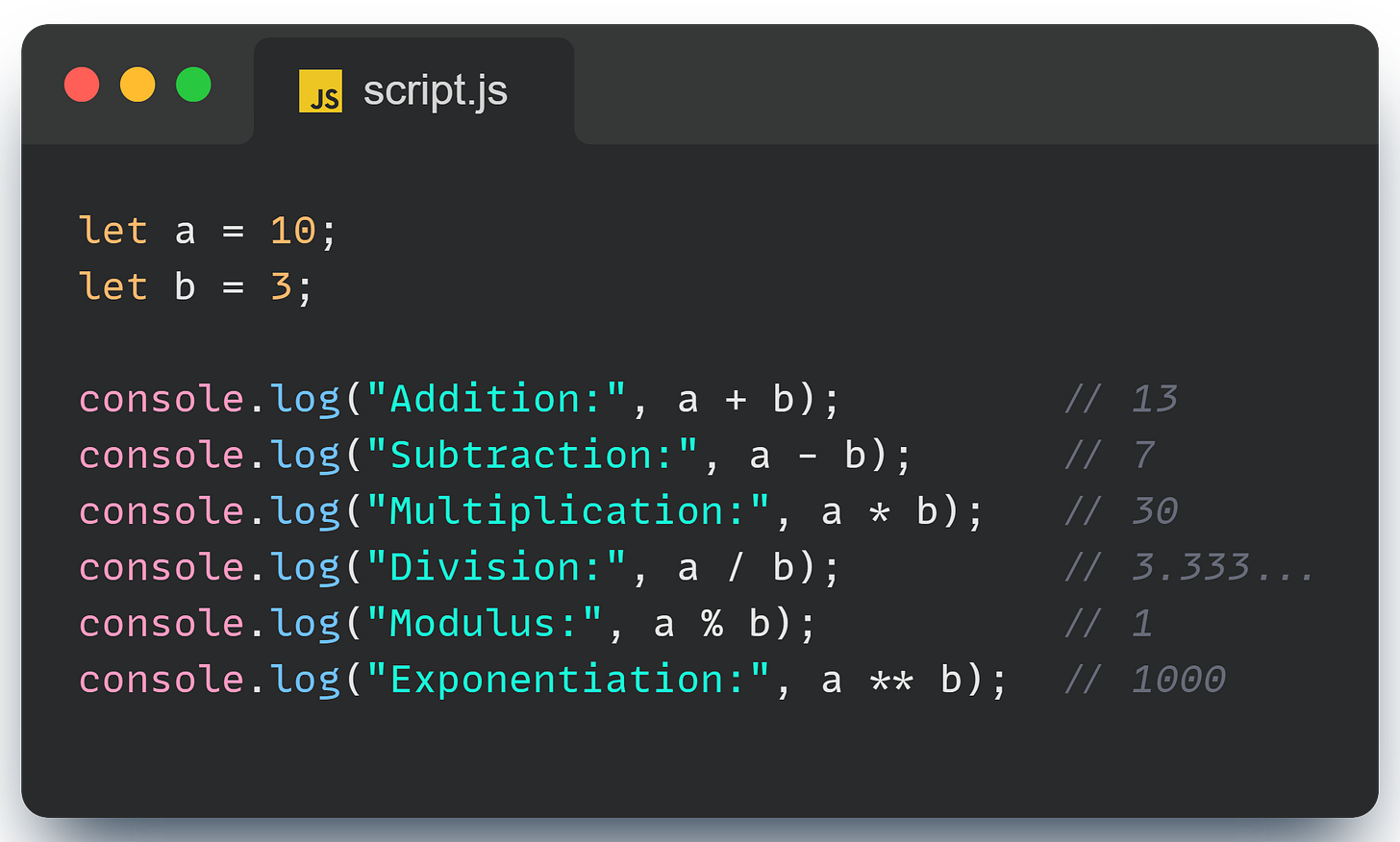
Arithmetic Operators: The Basic Building Blocks
Let's start with the basics: arithmetic operators. These are the bread and butter of any programming language, allowing you to perform calculations.
Here’s the deal: Division in JavaScript might surprise you if you’re used to languages with separate integer division operators. In JavaScript, if both numbers are integers and the result is a whole number, / acts like integer division. Otherwise, it gives you a floating-point number.
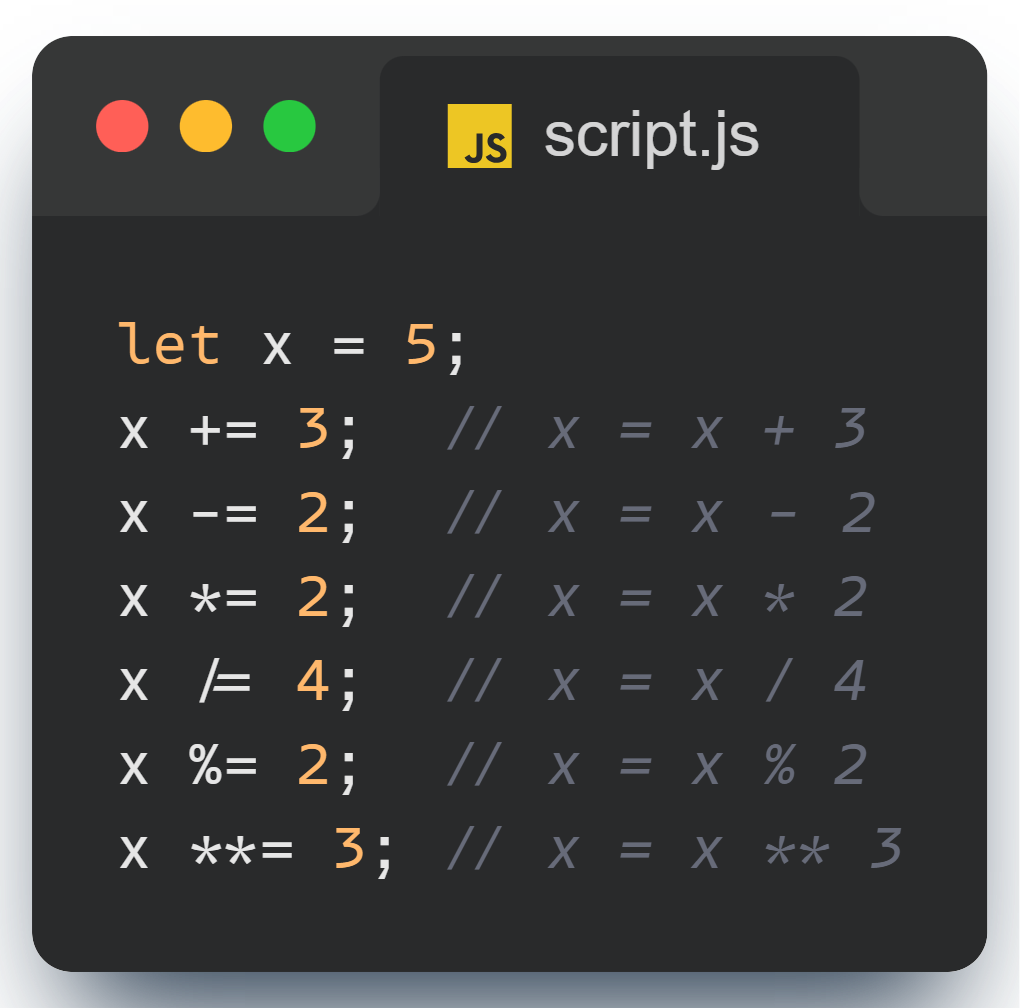
Assignment Operators: Keep It Short and Sweet
Assignment operators let you update the value of a variable in a concise way. Instead of writing out full expressions, you can just do this:
These shorthand operations save time and keep your code clean. Why write more when you can do it in fewer characters?
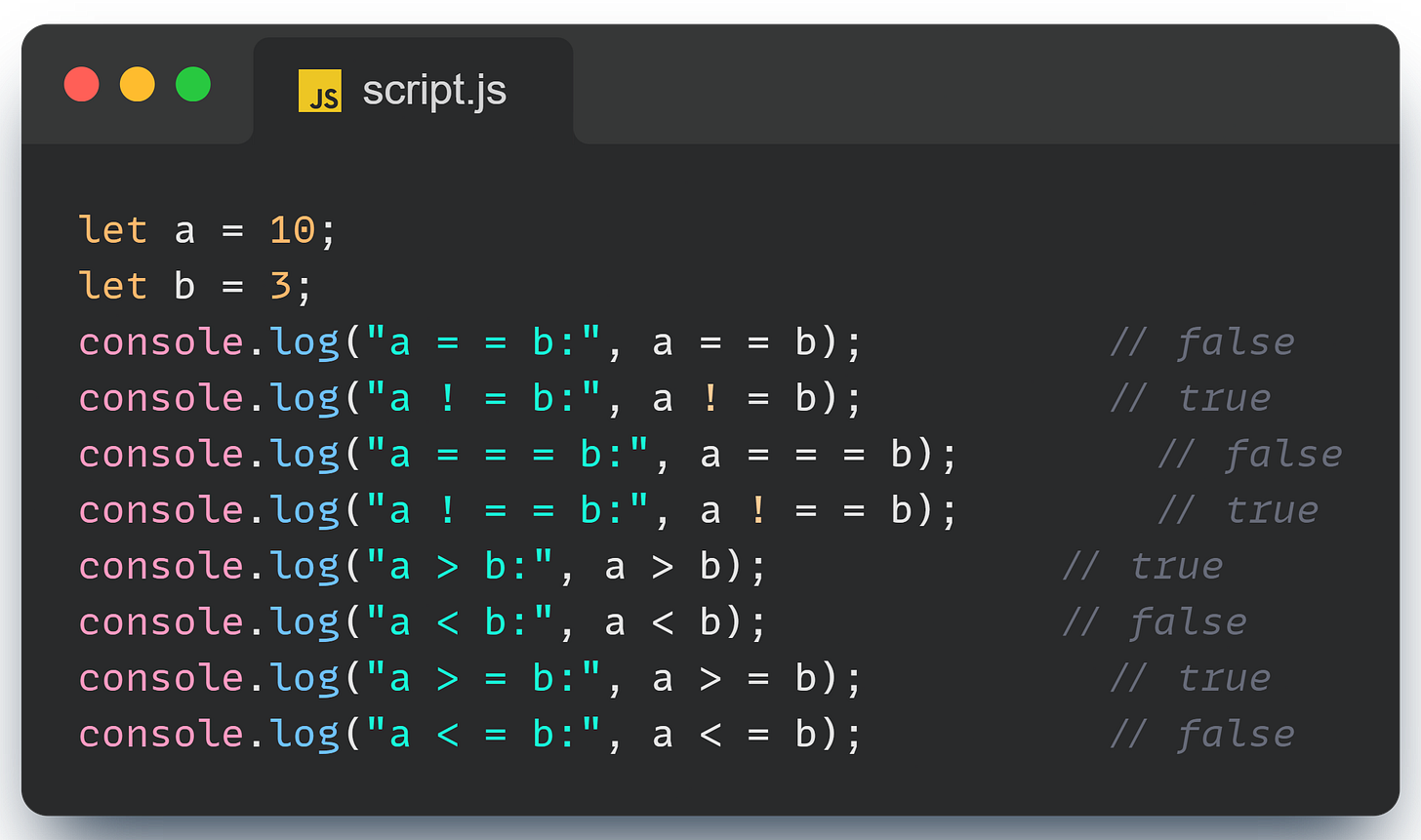
Comparison Operators: True or False?
Comparison operators are your go-to tools when you need to compare values.
Here’s a quick tip: == checks for equality with type conversion (loose equality), while === checks for strict equality without type conversion.
Use === when you want to avoid surprises!
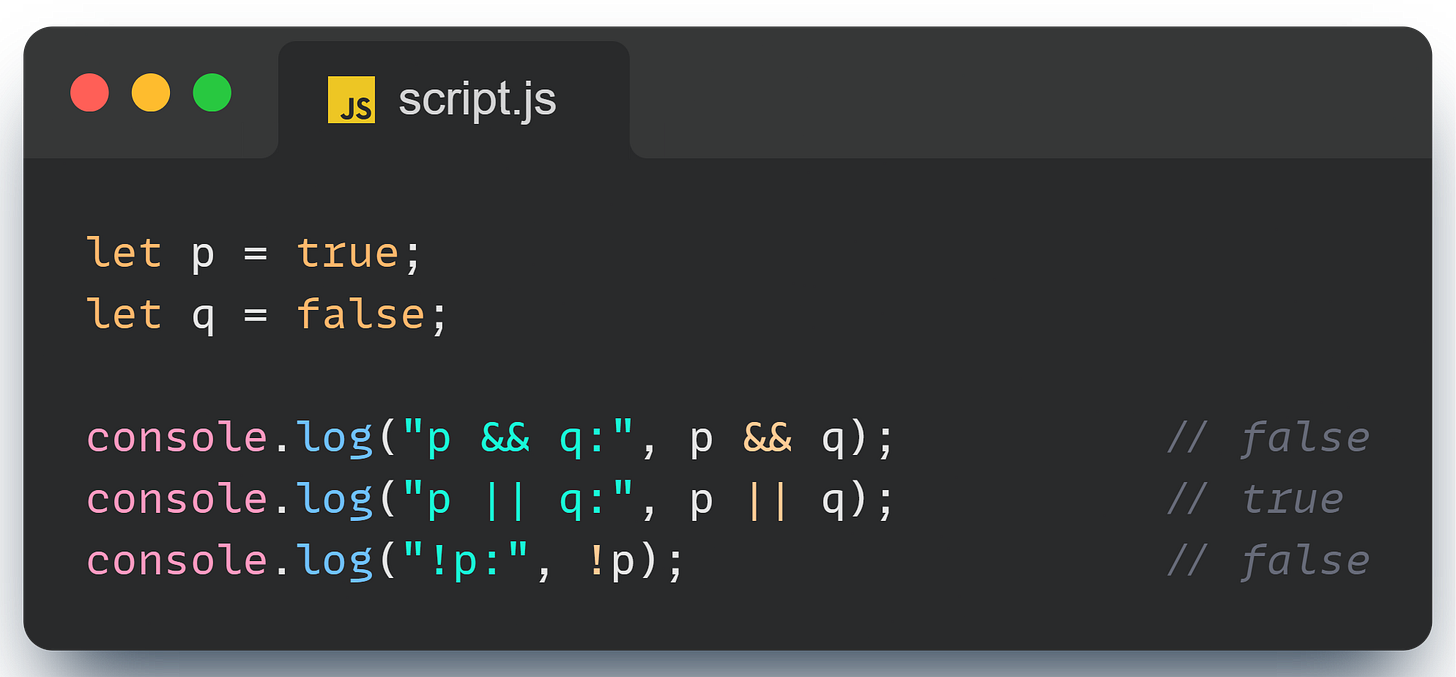
Logical Operators: Make Decisions with Ease
Logical operators help you make decisions based on multiple conditions.
These are super useful when you need to combine conditions, like checking if a user is logged in and has admin rights before allowing access to certain features.
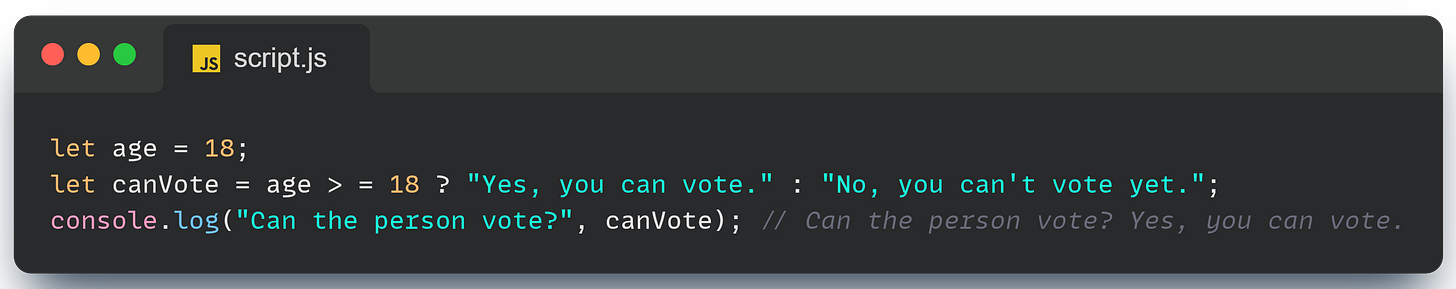
Ternary Operator: The Compact If-Else
The ternary operator is a shorthand way of writing an if-else statement. (you will understand the compactness when I’ll complete if else in my next article)
It’s perfect for simple conditions, making your code more concise and readable.
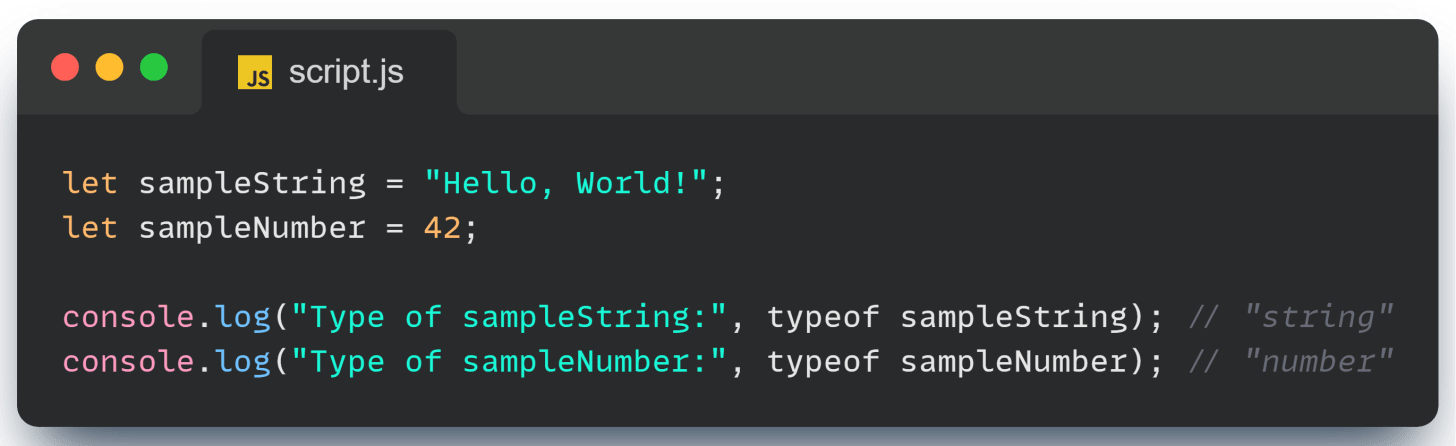
typeof Operator: What Type Is It?
We have already encountered this operator. Let’s look at it explicitly. The typeof operator is your friend when you need to check the type of a value.
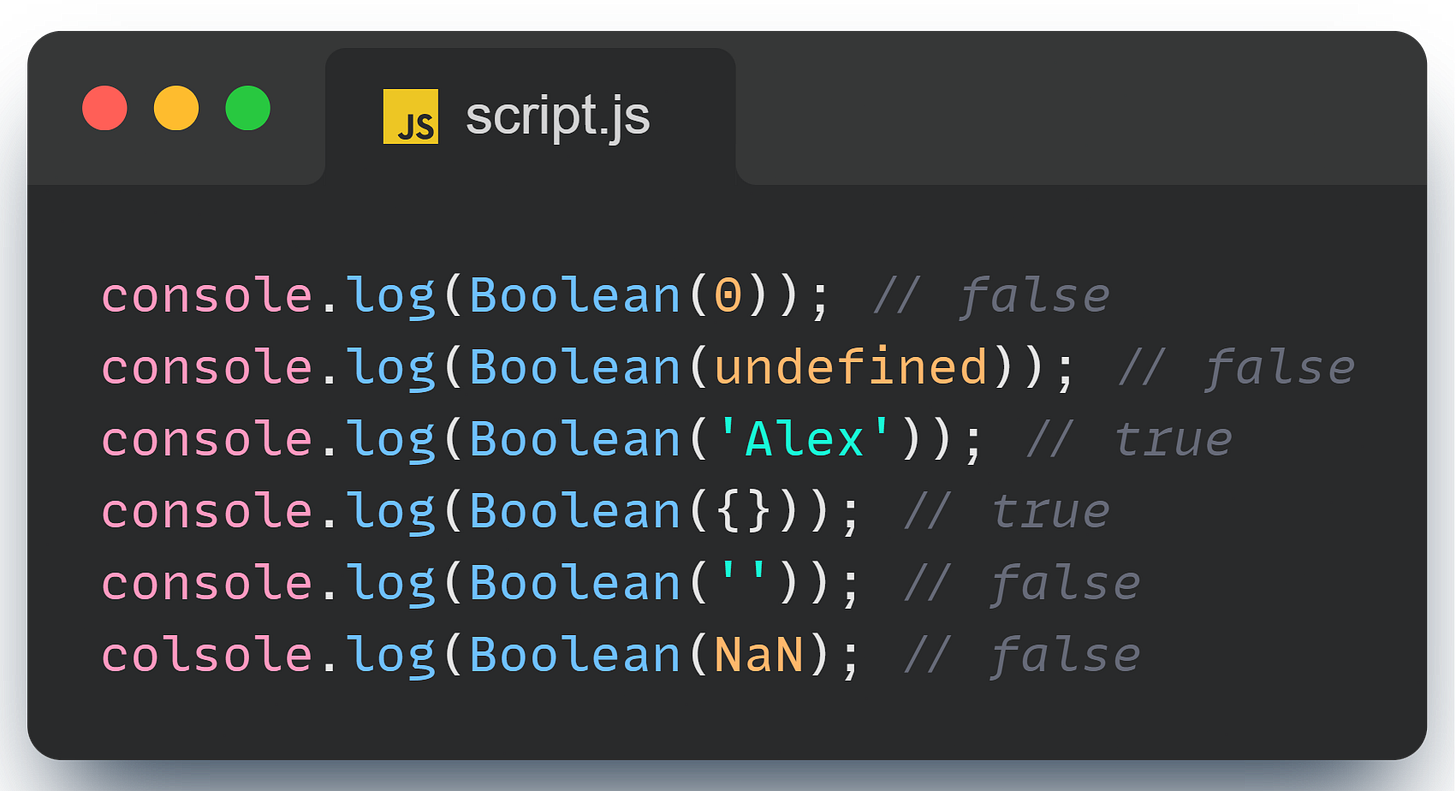
Special Cases: Truthy and Falsy Values
JavaScript has some quirky behavior with truthy and falsy values. Understanding these can save you from unexpected bugs.
There exists only five falsy values: 0, '', undefined, null, NaN (not a number).
Well, if you are confused, the next section will remove all your confusion!
Equality and Comparison Operators: A Closer Look
To wrap things up, let’s revisit the differences between == and ===, as well as != and !==. These operators can be tricky, but once you understand them, they’re incredibly powerful.
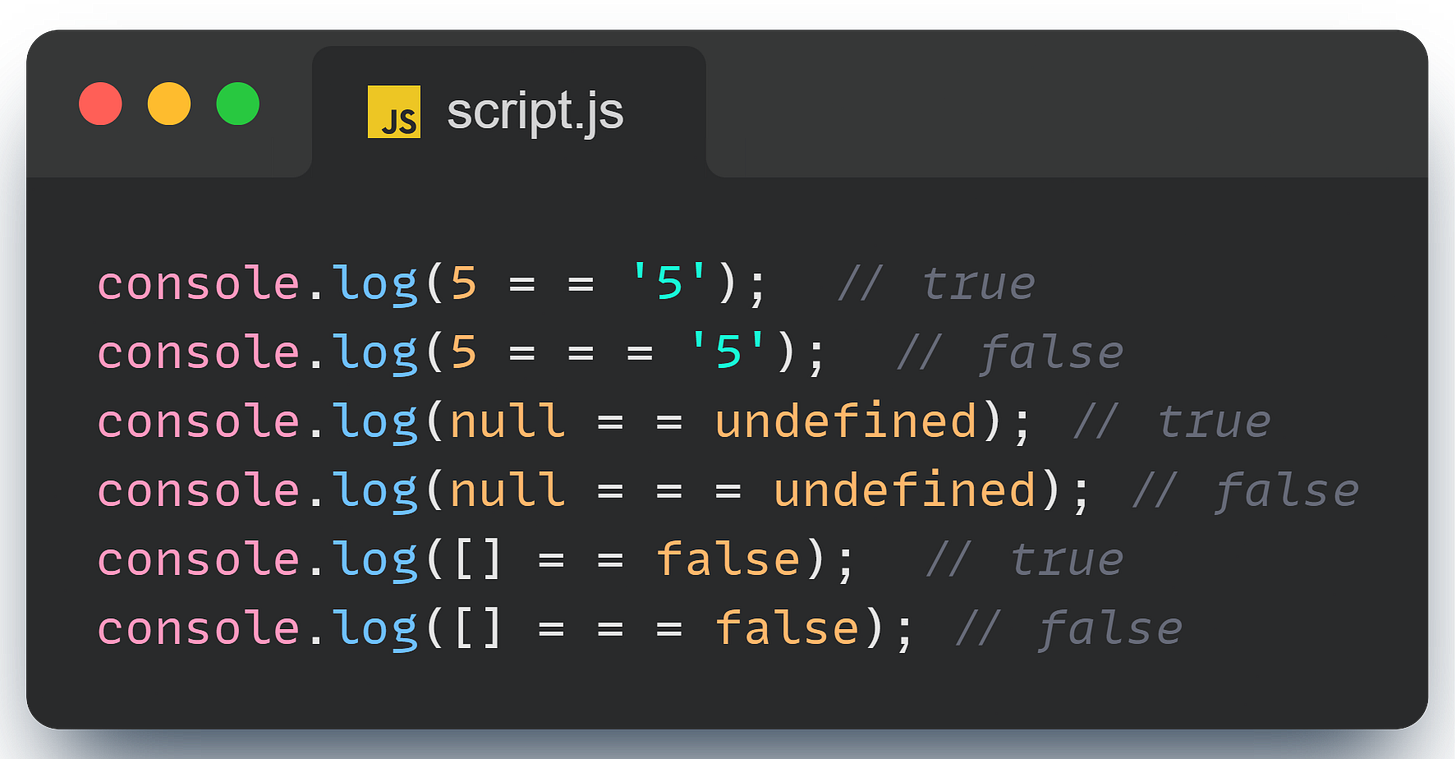
console.log(5 == '5'); // trueHere,
5(a number) is loosely compared to'5'(a string). JavaScript converts the string'5'to a number and then compares them, resulting intrue.
console.log(5 === '5'); // falseHere,
5(a number) is strictly compared to'5'(a string). Since they are of different types, the comparison returnsfalse.
console.log(null == undefined); // trueHere,
nullandundefinedare loosely compared. JavaScript considers them equal when using==, so it returnstrue.
console.log(null === undefined); // falseHere,
nullandundefinedare strictly compared. They are different types (nullis an object,undefinedis undefined), so it returnsfalse.
console.log([] == false); // trueHere, an empty array (
[]) is loosely compared tofalse. JavaScript converts the array to a primitive value (which is an empty string"") and then to a number (0), andfalseis also converted to0. Therefore,0 == 0results intrue.
console.log([] === false); // falseHere, an empty array (
[]) is strictly compared tofalse. Since they are of different types (an array vs. a boolean), the comparison returnsfalse.
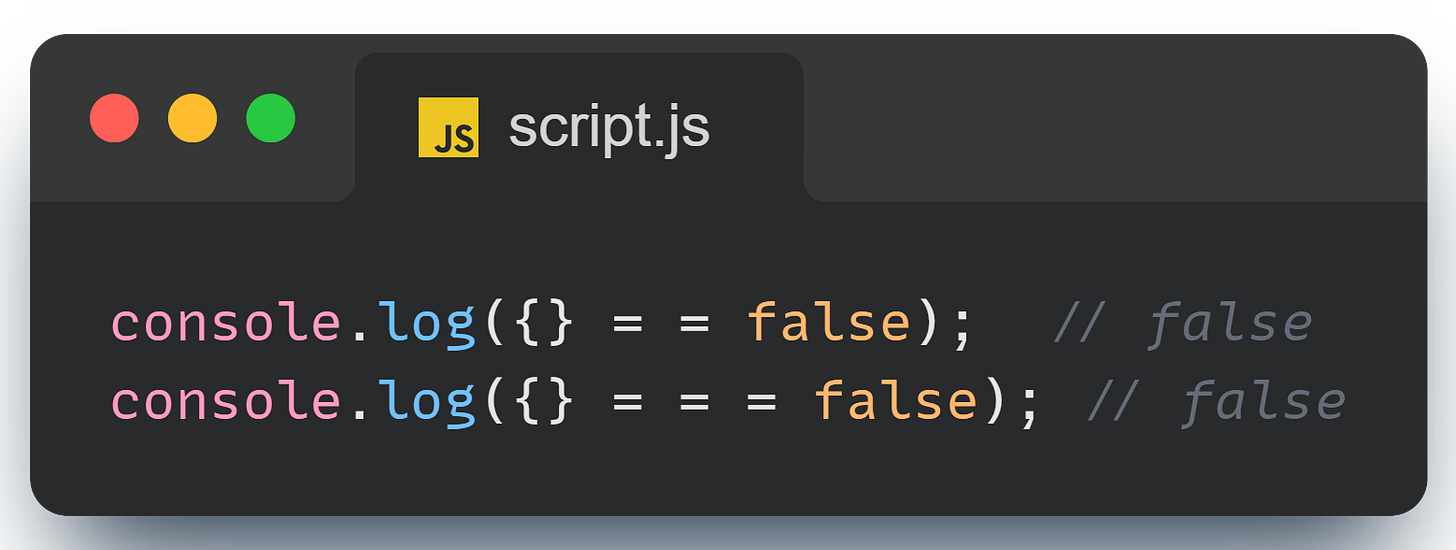
However, be careful with objects in JS (if you do not have any knowledge of objects, don’t worry! you can skip this for now - revisit once you have read about objects)
No matter what the equality is, we see that this always evaluates to false! The reason being, JS compares objects by reference and not by value! (remember this!)
Key Takeaways:
Use
==when you want to compare values, allowing for type conversion.Use
===when you want to ensure that both the value and type are the same. This is usually safer and recommended in most cases to avoid unexpected results due to type coercion.
Conclusion
And there you have it—an in-depth look at JavaScript operators, and a deeper understanding of let, const, and var. Understanding these fundamental concepts is key to mastering JavaScript and writing clean, efficient code.
Keep experimenting, and stay tuned for the next article where we’ll dive into functions and the magic of this in JavaScript. Until then, happy coding! 🎉