Vue.js Chronicles (Part I) - Build your first Vue app!
Topics - Build your first Vue app!, Learn Methods and access the instance data
What’s Vue.js All About?
Imagine building a website is like building a house. Vue.js is like having a super flexible toolkit that helps you design the interior with ease. Vue.js is a popular JavaScript framework used to create user interfaces (UIs) and single-page applications (SPAs). It’s great for making things look and work smoothly without a lot of effort.
Unlike other heavy frameworks, Vue.js is like your go-to toolbox that you can start small with and then add more tools as you need them. Whether you’re adding just a small feature or building a full-blown app, Vue.js fits right in. It's easy to learn, and once you get the hang of it, you’ll wonder how you ever lived without it!
Quick Setup with CDN: The Easy Way to Get Started
Let’s say you’re hosting a party and need to order pizza. Instead of baking it from scratch, you just order it from your favorite pizzeria — it’s faster and saves you the hassle. Using a CDN (Content Delivery Network) to get Vue.js is like ordering that pizza. You get what you need quickly, without dealing with complicated setups.
How Does a CDN Work?
A CDN is like a chain of pizza shops scattered across the country. When you order a pizza, it’s delivered from the nearest shop, so it arrives hot and fast. Similarly, when you include Vue.js via a CDN, your browser grabs it from the nearest server, making your website load faster. Plus, if your neighbors (other websites) already have that same file, it’s even quicker!
Installing Vue.js with a CDN
Adding Vue.js to your project with a CDN is as easy as adding a topping to your pizza. Here’s how you do it:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script>
In this example, unpkg is used to load Vue.js. However, you can also use other CDNs like jsdelivr or cdnjs. These CDNs host popular libraries and frameworks, so you can easily include them in your project by simply adding a script tag.
Why Use a CDN?
Using Vue from a CDN is super convenient because there’s no need for a build step. That means you can start coding immediately without worrying about setting up a development environment. This approach is perfect for adding interactivity to a static HTML page or integrating Vue.js with a backend framework.
Here’s a full example using this setup:
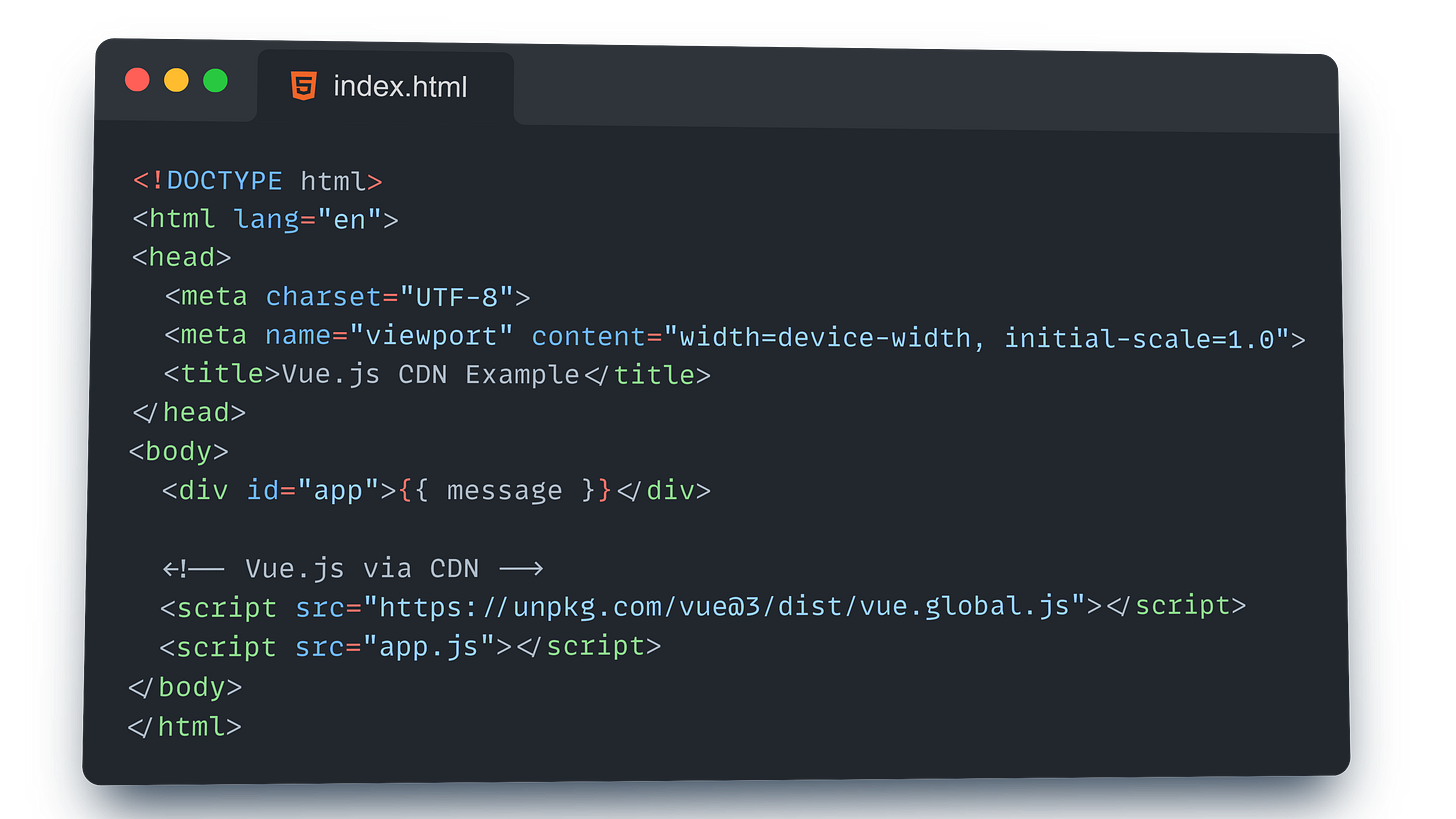
Create a index.html document and add Vue.js using CDN
Create a style.css file and add it to html document if you want to add any styling. (I will not include any CSS for this example but you can always try and beautify what you see!)
Create a app.js file and in this file we will write the first few lines of code in Vue.
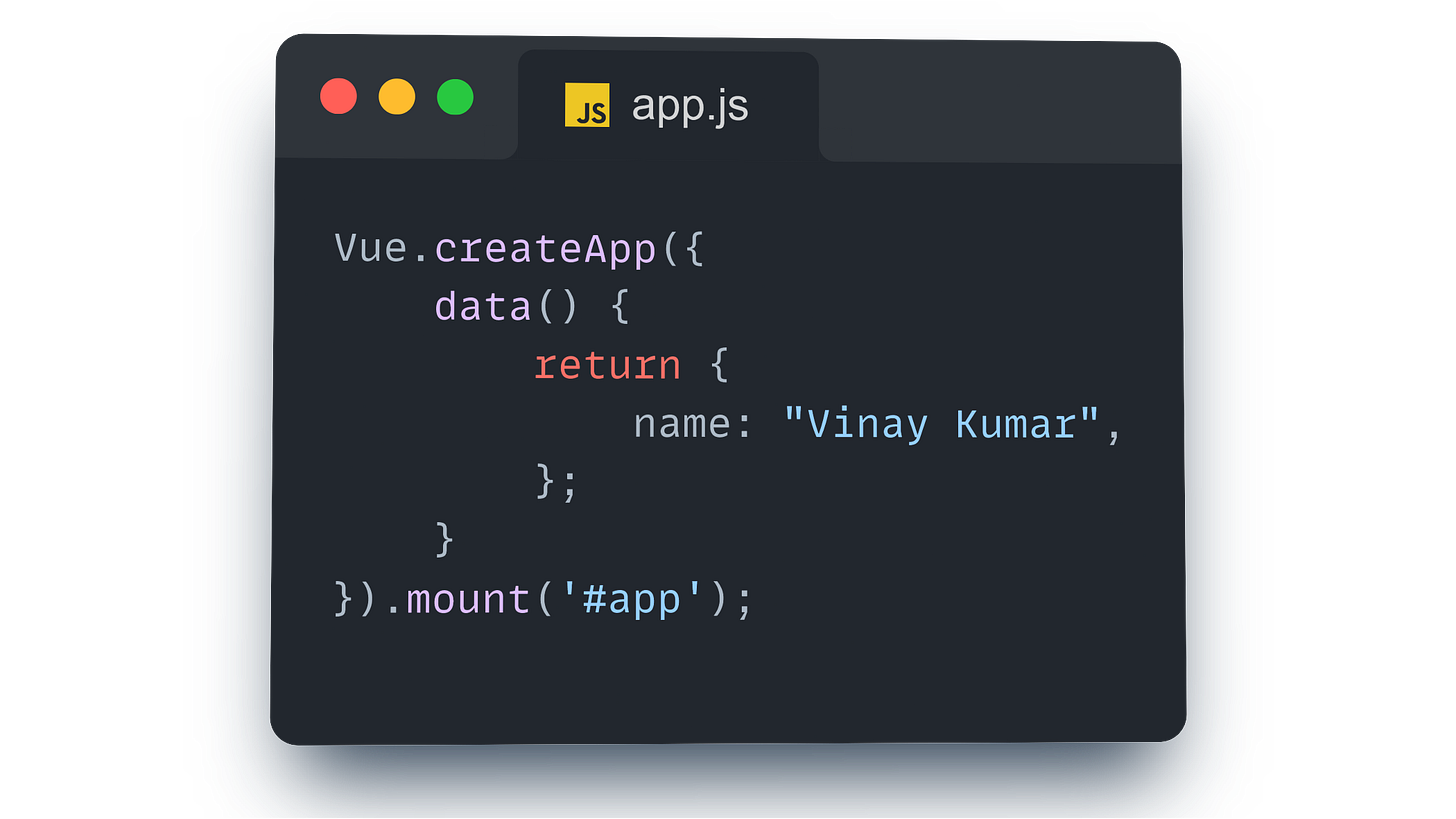
Now that we are done with the basic set up, let us create a Vue app in the app.js file!
Creating our first Vue app!
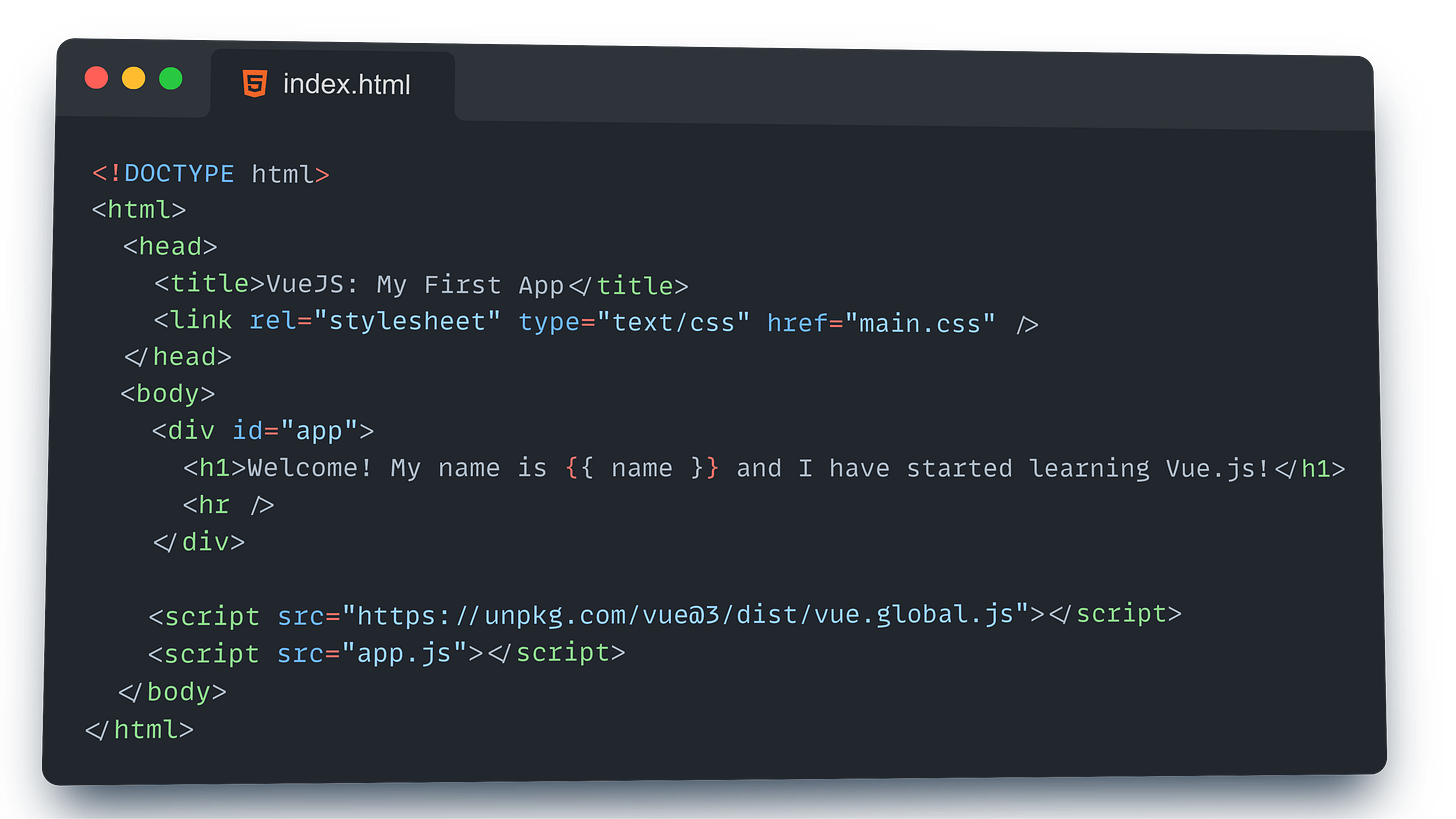
Welcome to your first steps in learning Vue.js! Let’s walk through building a simple Vue app that displays a message on the page. The code that I will write will be broken code step by step, so you understand what’s happening at every stage.
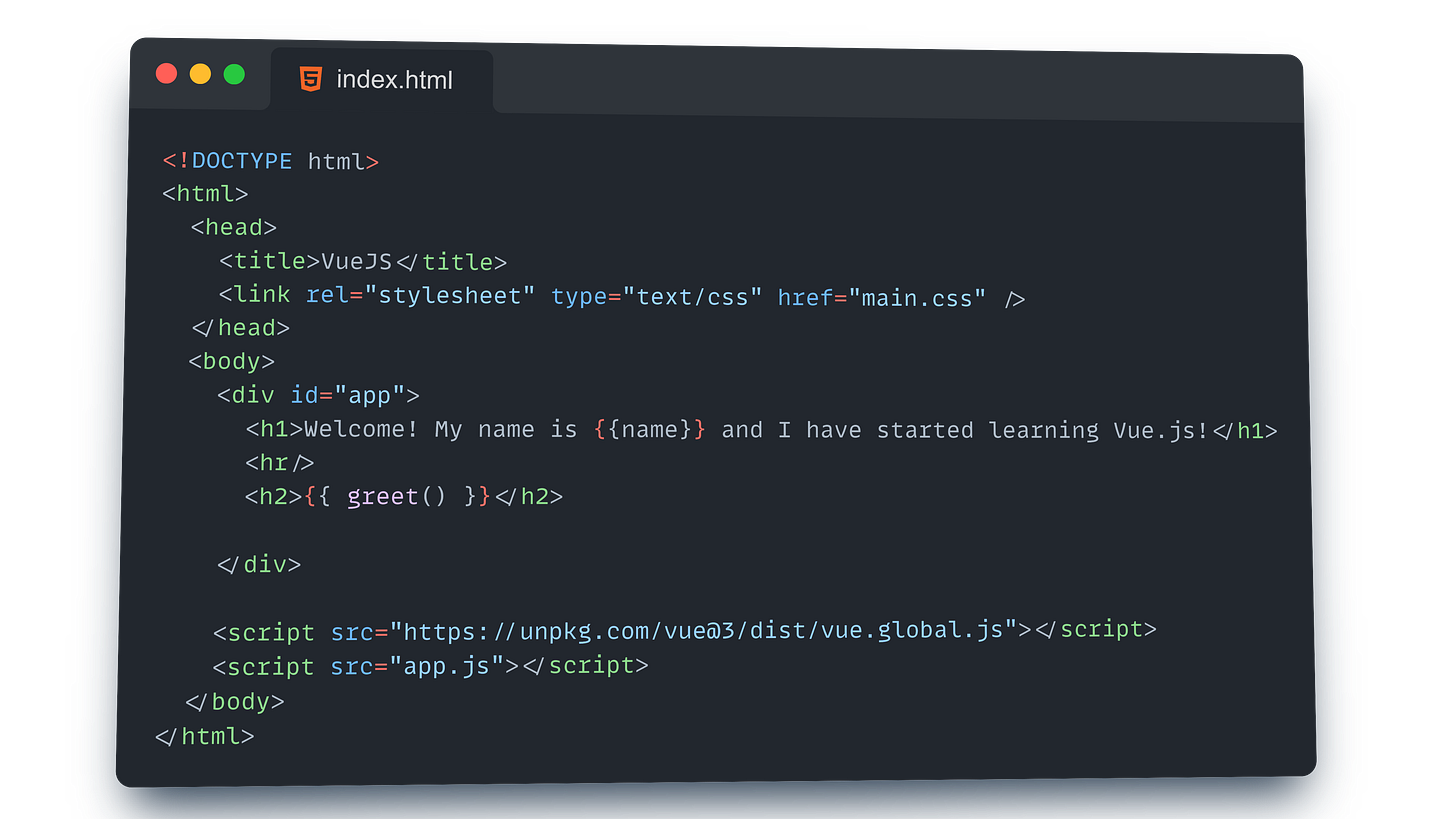
Setting Up the HTML Structure
First, we’ll create the basic structure of our webpage. This is like laying the foundation of a house before adding all the cool features.
Let us now breakdown the code step by step:
Writing the Vue.js Code
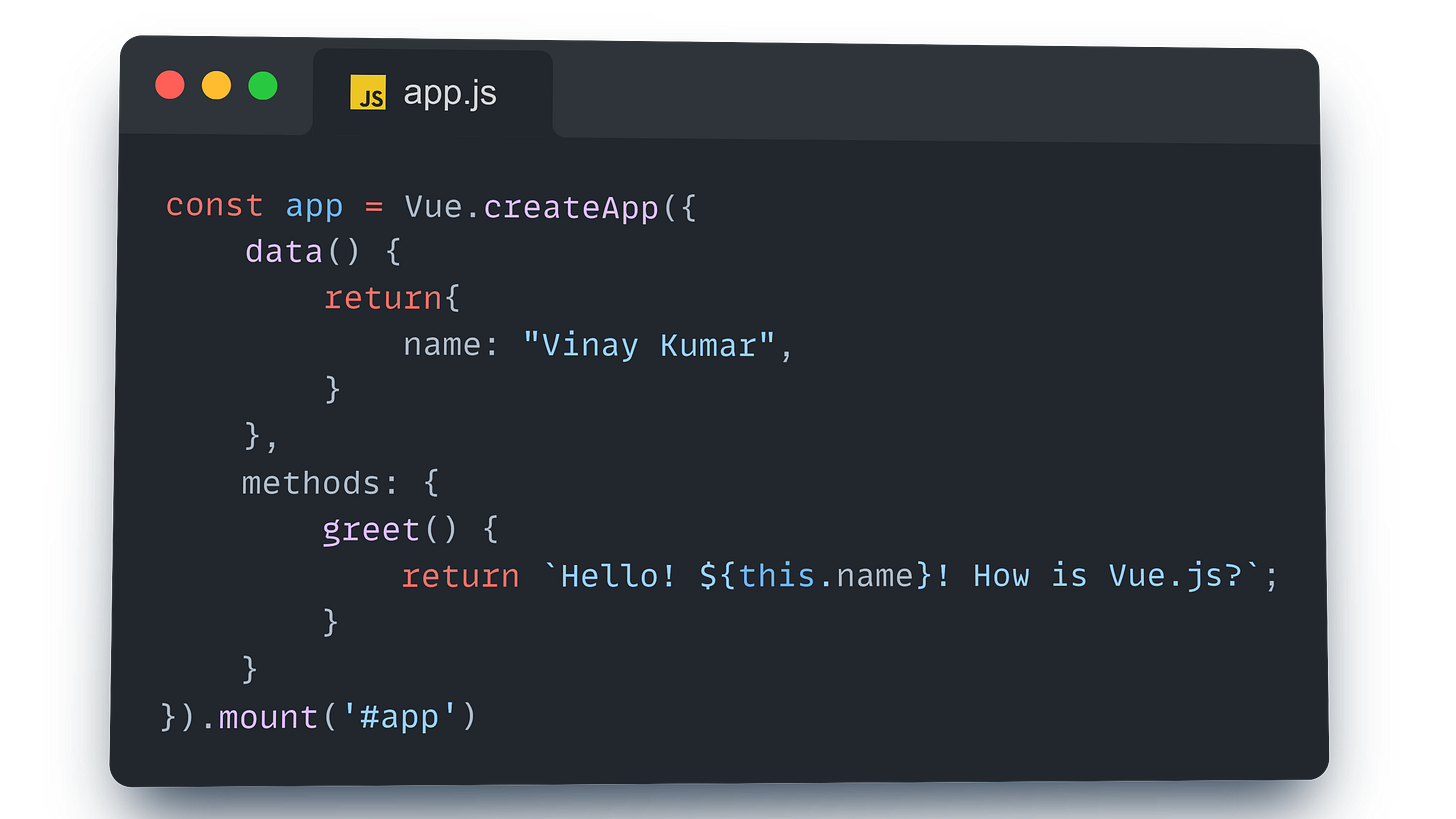
Next, let’s create the app.js file where we’ll set up our Vue app:
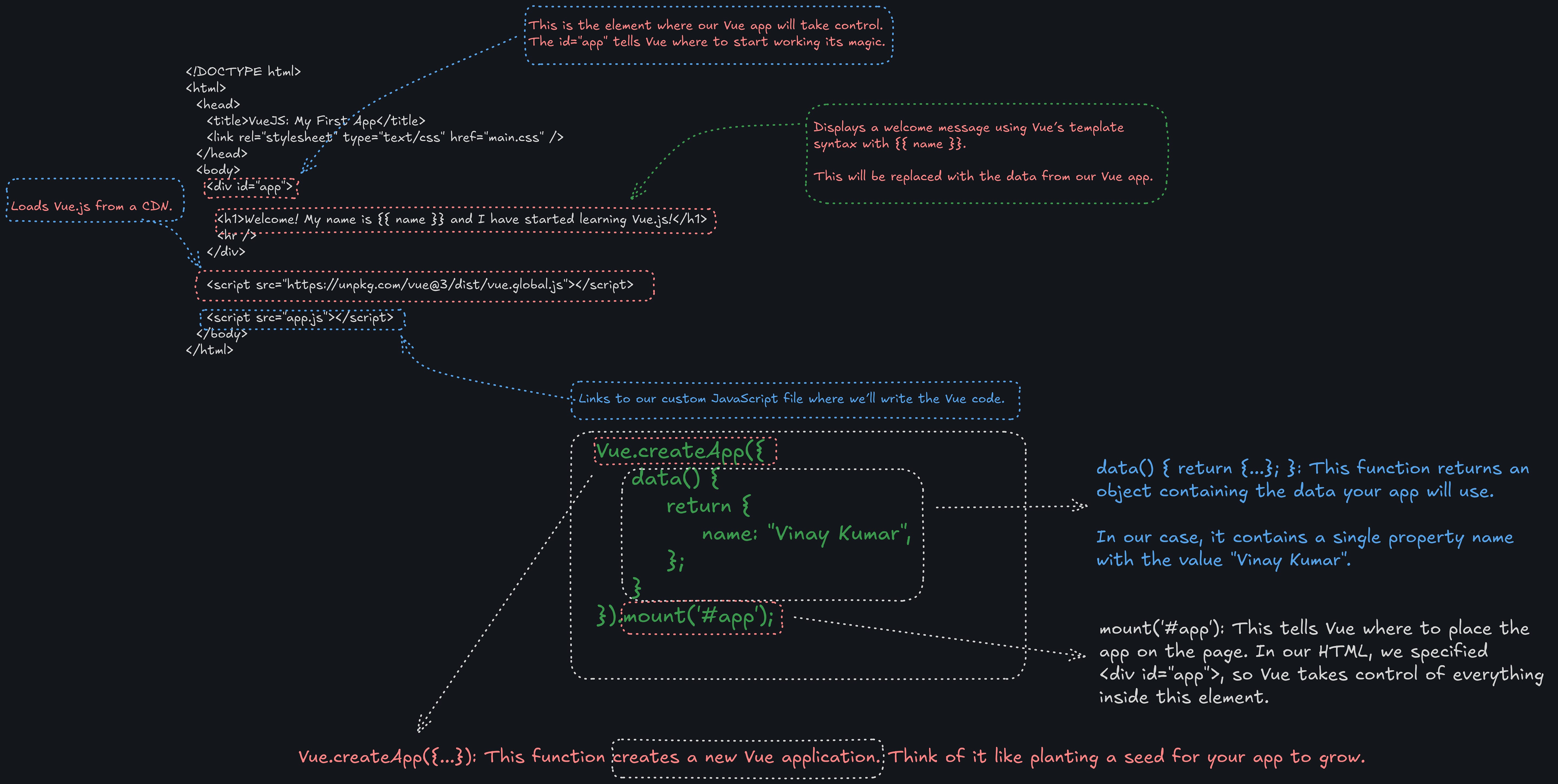
Here’s what’s happening:
Bringing It All Together
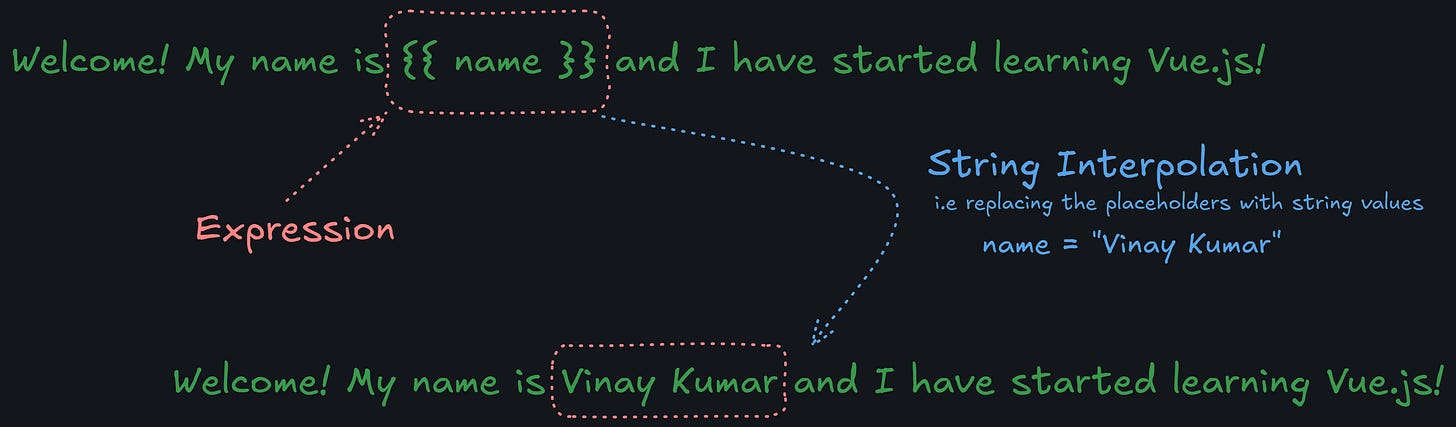
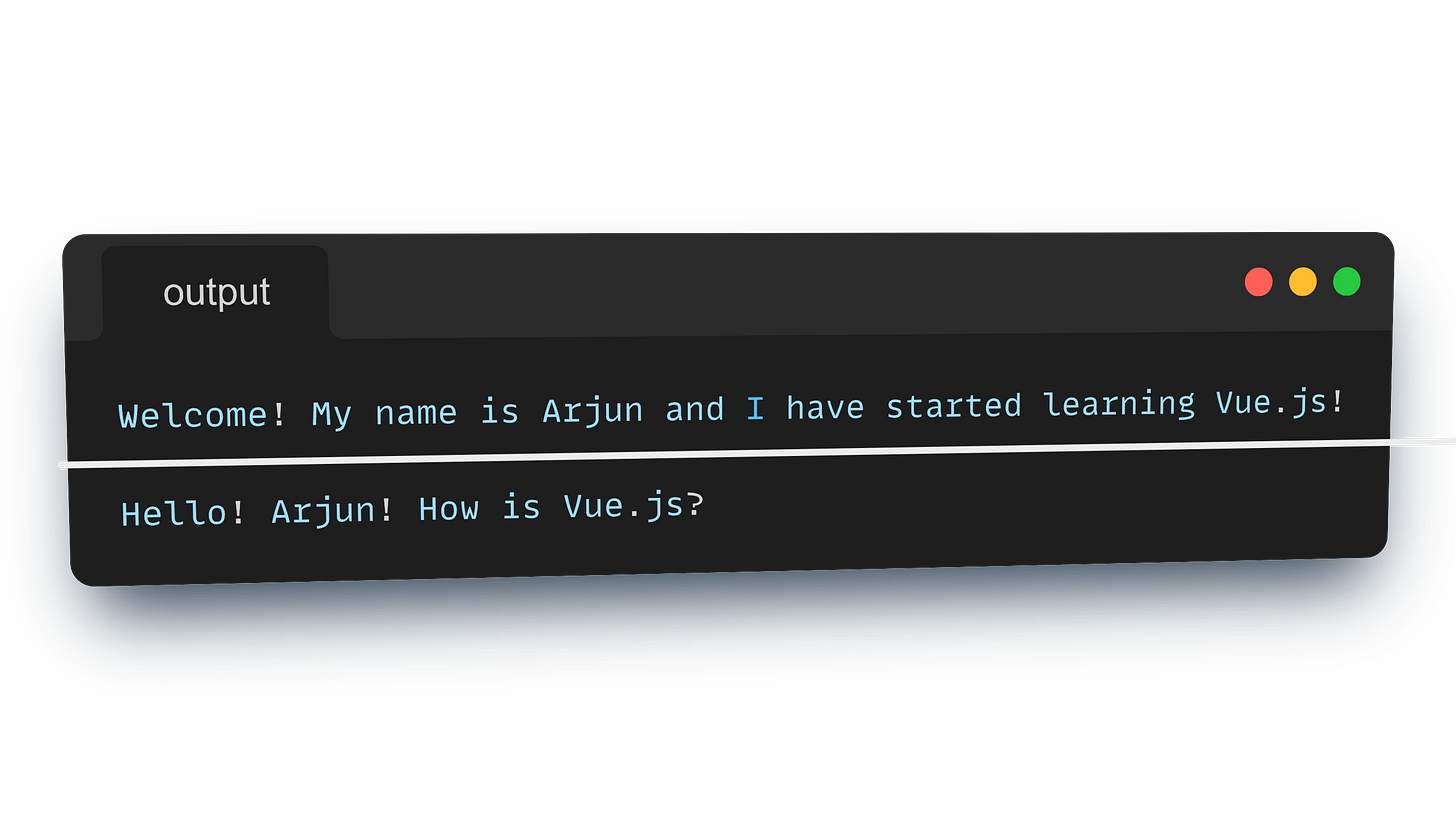
When you open your HTML file in a browser, Vue.js takes over the <div id="app"> element. The placeholder {{ name }} in the HTML will be replaced with the value from the name property in your Vue app. So, you’ll see:
Welcome! My name is Vinay Kumar and I have started learning Vue.js!
And that’s it! You’ve just built your first Vue.js app!
Note: EXPRESSIONS ( i.e. content inside {{}} are always rendered and displayed on the browser!)
Methods in Vue.js
In Vue.js, methods are functions defined within a Vue component that can be used to perform actions or calculations. Methods are useful for handling user interactions, manipulating data, or performing other operations within your component.
Defining Methods
Methods are defined inside the methods option within a Vue instance. You can define any number of methods, and they can be accessed using the this keyword, which refers to the Vue instance.
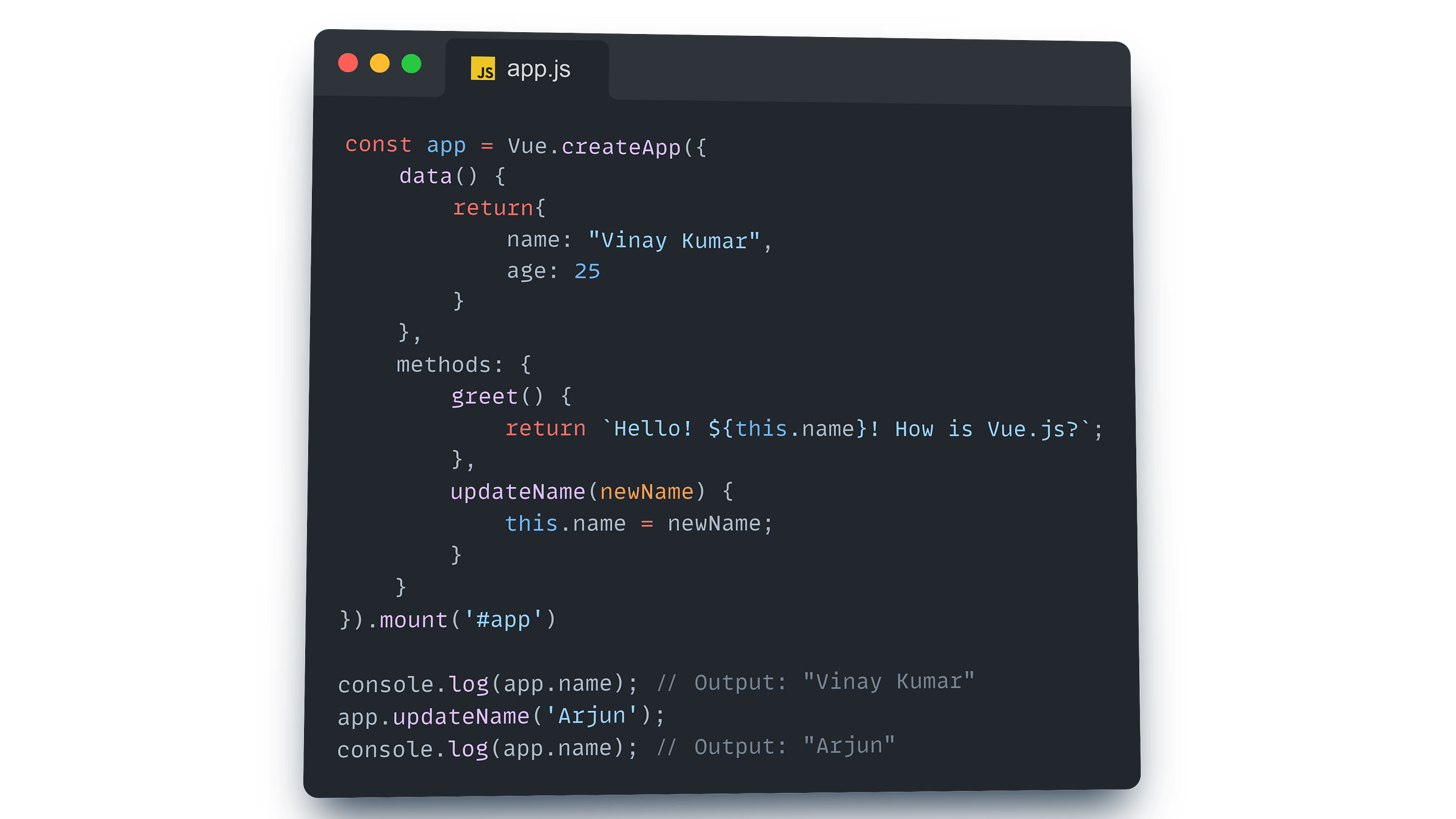
Example: Using Methods in Vue.js
Let’s look at an example where we have a simple Vue instance that introduces methods in the code:
HTML Structure
In this example:
Data: We have a
nameproperty in thedataoption.Method: The
greetmethod returns a greeting message using thenameproperty.
In the template, we can directly call the greet method within {{ }} to display the greeting message.
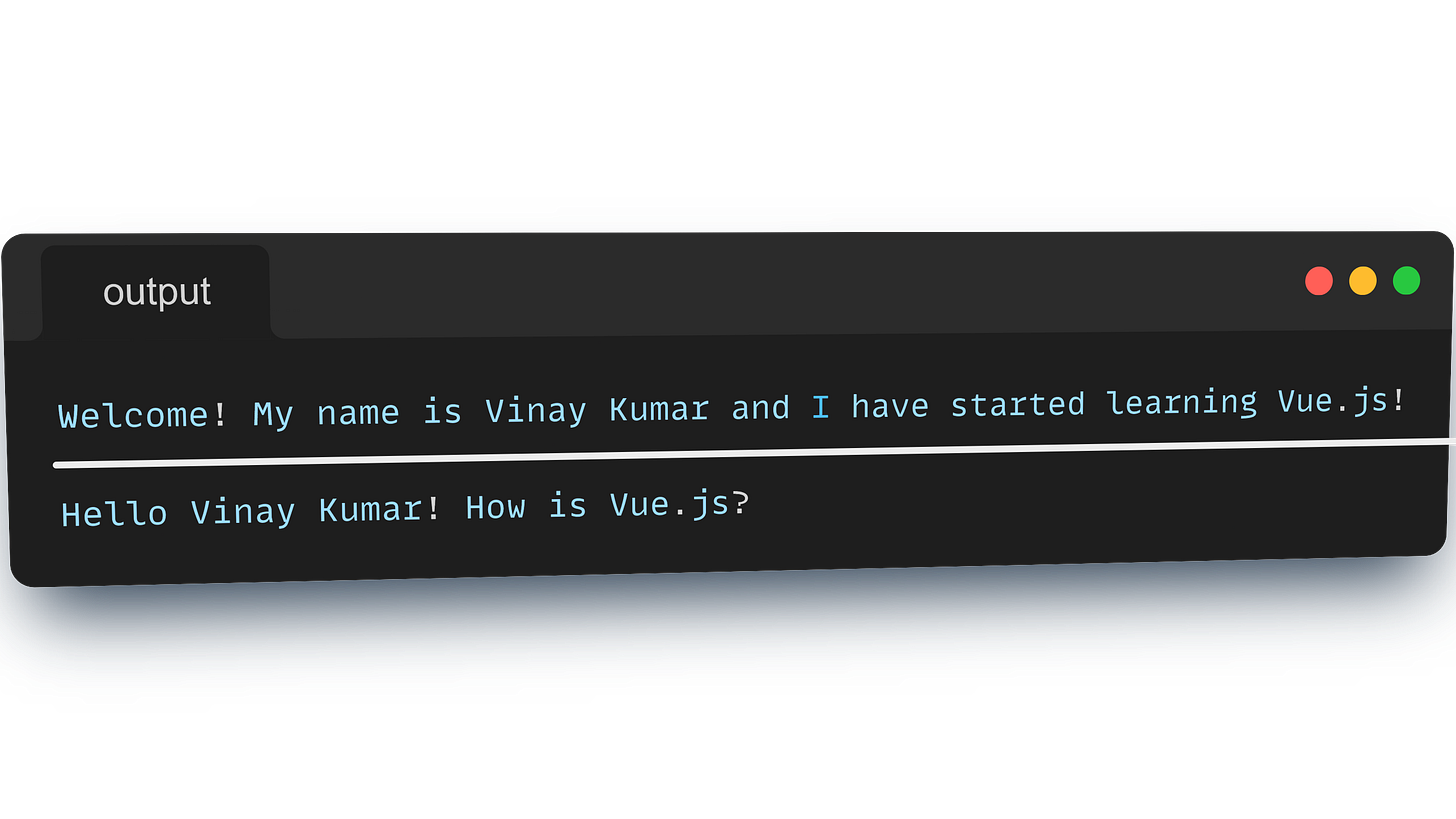
<h2>{{ greet() }}</h2>The output that you get after you run the .html file is:
Accessing Vue Instance Data
In Vue, the data defined in the data() function of an instance is easily accessible both within the template and the instance itself. This is because Vue proxies the data properties, allowing direct access without having to explicitly refer to the data object.
Example: Accessing Instance Data
We have already seen such an example! In the previous section, when we created the method greet(), we did access the instance data using the this keyword.
Let us now take a similar but a slightly different example and understand what exactly did we do.
Here’s what’s happening:
Accessing in Template: In your HTML, you can access
nameandagedirectly using{{ name }}and{{ age }}.Accessing in Methods: Within the Vue instance, you can access
nameusingthis.name.Updating Data: You can update
namedirectly withthis.name = 'New Name'.
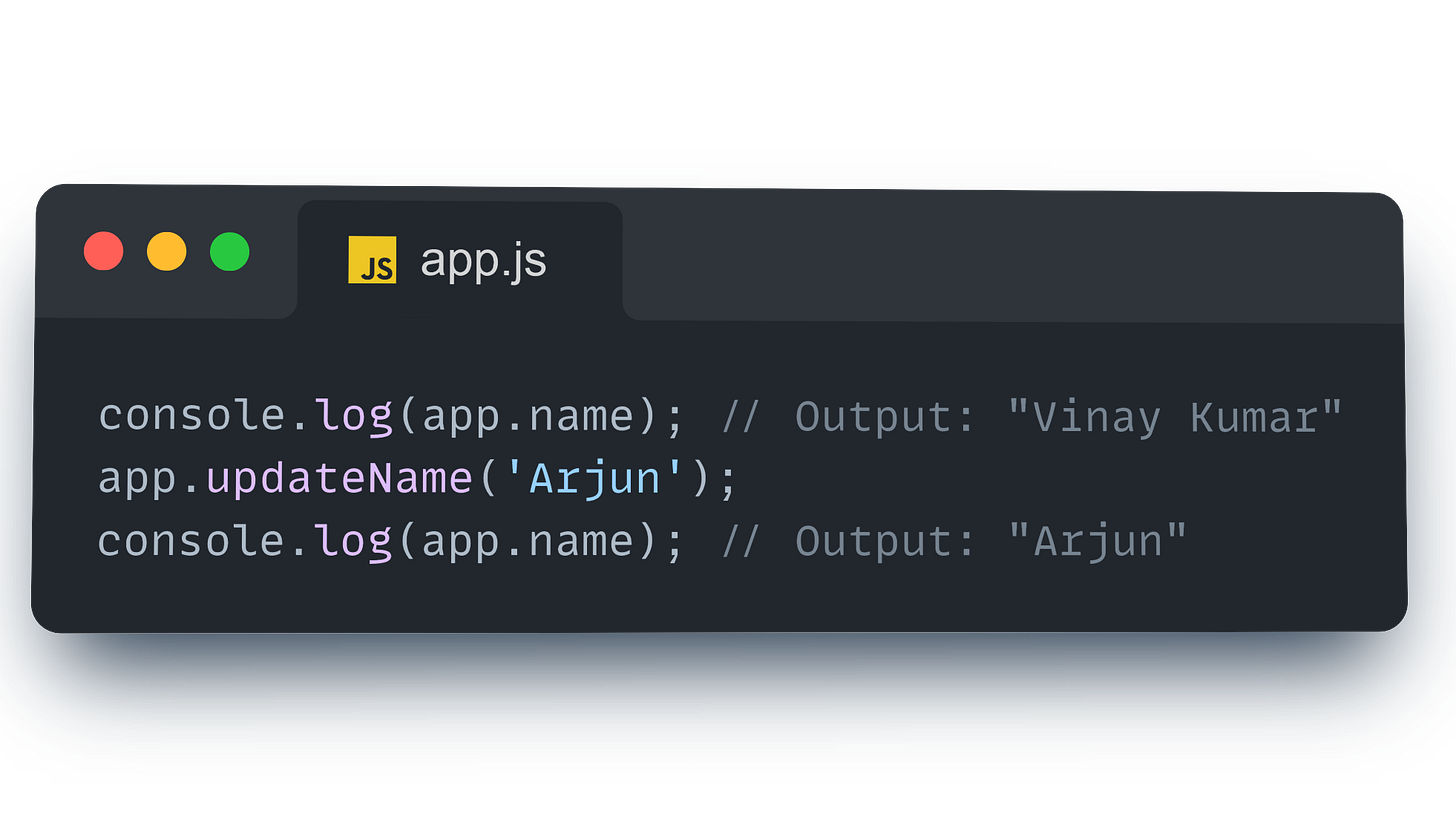
Accessing Instance Data Directly
You can also access the Vue instance’s data directly using the instance variable (e.g., app):
Proxy Getters and Setters in Vue
Vue’s reactivity system is built around the concept of proxy getters and setters. This mechanism allows Vue to intercept changes to data properties and trigger the necessary updates to the DOM.
How Proxy Works
When you define a property in the data() function, Vue creates a proxy for that property:
Getter: When you access a property (e.g.,
this.name), Vue intercepts the access using a proxy getter. This allows Vue to track dependencies, so it knows which parts of the DOM need to be updated when the data changes.Setter: When you modify a property (e.g.,
this.name = 'Arjun'), Vue intercepts the change using a proxy setter. This allows Vue to trigger reactivity and update the DOM accordingly.
Let’s break down the concept using a simplified analogy:
Getter:
Imagine you’re reading a book, and each time you open the book (access data), a library notes which book you’re reading (dependency tracking).
In Vue, when you access
this.name, Vue knows that the template depends onname.
Setter:
Now, imagine you decide to change the book’s title. The library immediately updates its records (DOM updates).
In Vue, when you change
this.name, Vue updates the DOM wherevernamewas used.
As a result the output that we get is as follows:
How Vue Uses Proxy to Access Data
With proxy getters and setters, Vue can:
Track Dependencies: When a component is rendered, Vue keeps track of which data properties are used, so it knows what to re-render if those properties change.
Trigger Reactions: When data changes, Vue automatically re-renders the parts of the DOM that depend on the changed data.
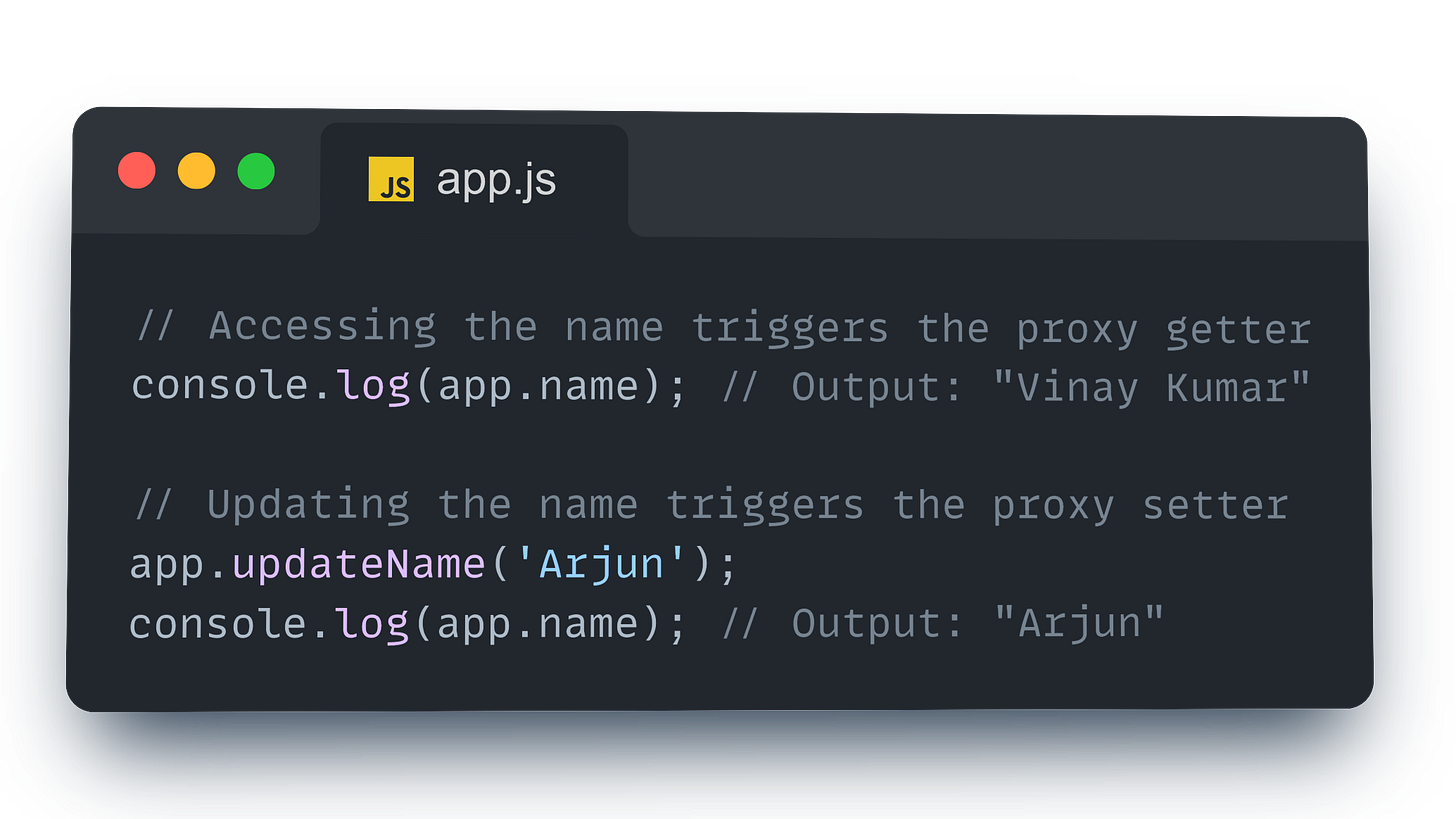
Example in Action
Here’s the code with comments explaining proxy behavior:
In the code above:
Getter: When
app.nameis accessed inconsole.log(app.name), Vue triggers the getter to track the dependency.Setter: When
app.updateName('Arjun')is called, Vue triggers the setter, updatingnameand re-rendering the part of the DOM that displaysname.
THUS,
Vue uses proxy getters and setters to manage reactivity, making it easy for developers to work with data directly without worrying about manual DOM updates. The simplicity of accessing and modifying instance data directly, combined with Vue’s automatic DOM updates, is what makes Vue so powerful and developer-friendly.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You've taken the first step in your Vue.js journey by understanding what Vue.js is, how to set it up using a CDN, and how to build your first Vue app. We explored the simplicity of integrating Vue into a project with just a few lines of code, without any complex build steps. You also learned how Vue allows you to manage dynamic data and update the DOM with minimal effort, making it a powerful tool for creating responsive and interactive web applications.
As you dive deeper into Vue, remember that this is just the beginning. The flexibility and ease of use that Vue.js offers will open up countless possibilities for your web development projects. Keep experimenting, and soon, you’ll be building even more advanced and dynamic applications with Vue.js.
Happy coding, and welcome to the world of Vue.js!